Capability Breakdown
Quicklime & Calciment® LKD vs. Portland Cement
The Right Solution to Save Time & Money When Weather is a Factor
Lime-based products are fast and effective at drying, modifying and stabilizing wet, unworkable soils. Chemically drying soils occurs when lime-based products are applied to wet soils to reduce the free (non-chemically bonded) water in the soil. by driving off moisture in the soil, they can achieve optimal moisture content as determined by the soil’s moisture-density relationship, as well as strength and compaction requirements. Lime-based products decrease downtime due to wet weather and extend the working season thanks to heat generation via exothermic reactions that are a natural occurrence of the hydration process.
Faster than Cement at Drying All Soil Types
Mintek offers a variety of products, including quicklime fines, pebble quicklime and Calciment® LKD (a unique blend of calcium oxide and pozzolans) to meet a variety of job site applications. These lime-based solutions accelerate drying thanks to the availability of calcium oxide in the product. Once applied and properly hydrated, Quicklime absorbs over 30% of its weight in water drawing moisture from the soil. Additionally, the hydration process creates exothermic reactions which cause heat and steam that drives off additional moisture. These attributes make lime-based products the most effective drying reagents used in soils.
Before:
After:
Summary
Both quicklime and Calciment® LKD provide benefits over Portland cement, including:
- Faster drying of wet, unworkable soils
- Dramatic reduction of shrink/swell potential of clay-based soils
- Short and long-term strength gains
- Less downtime due to inclement weather
- Longer construction season due to the ability to work in cold, wet conditions
- Help keep projects on track to save time and money
Better than Cement at Modifying Clay Soils
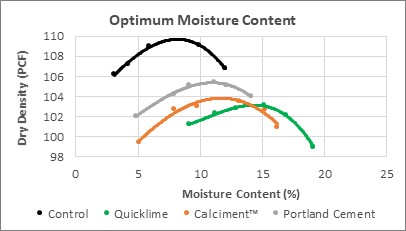
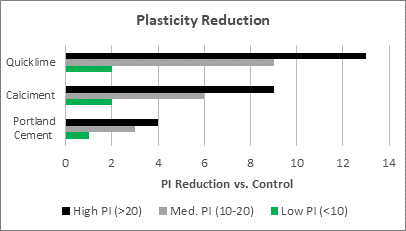
The high concentration of oxides present in quicklime and Calciment® LKD dramatically reduce the plasticity of clay soils. This plasticity reduction of the soil, determined by calculating a soil’s Plasticity Index (PI), makes handling and compaction easier, reduces or eliminates the shrink/swell potential especially after wet/dry and freeze/thaw cycles and provides an improved working platform during construction. The modification of the clay molecules also raises the optimum moisture content (OMC) of the soil further reducing the amount of soil drying needed to achieve compaction.
Optimum Moisture Content (OMC)
Plasticity Reduction
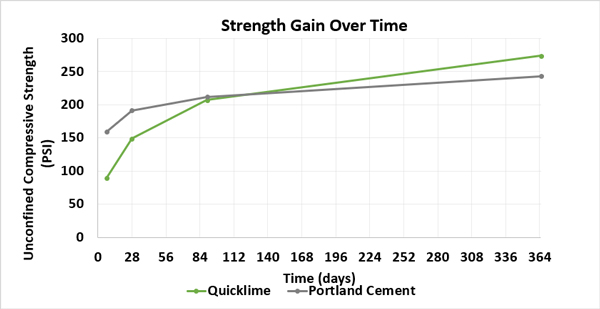
Quicklime and Calciment® LKD Offer Short & Long Term Strength Gains
Adding quicklime and Calciment® LKD to weak, problematic, fine grained soils will positively alter their engineering properties. Treatment will transform the soil, increasing its compressive strength, rutting resistance, and freeze/thaw durability. However, unlike Portland cement, treated soils, whose strength gains rapidly taper off, quicklime and Calciment® LKD treated soils can continue to gain strength for more than a year by reacting with the natural pozzolans present in the soil (and supplemented when using Calciment® LKD) allowing for lower dosage rates to achieve better long-term results over Portland cement.
Improved Workability vs. Portland Cement
Quicklime and Calciment® LKD are not as time-sensitive as Portland cement, which must be placed, mixed and compacted within three hours of application. This narrow window does not provide much time for correction should equipment or logistical issues arise. Conversely, soil treated with quicklime and Calciment® LKD can be handled over a day after application. Also, quicklime and Calciment® LKD out perform Portland cement for extending the working season into the cold/wet winter months. This is due to the substantial heat generated as it hydrates, which is capable of driving the desired chemical reactions even in frozen soils.
Frozen, unworkable soil
Quicklime being laid on frozen soil
